Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable water conservation technique that collects, stores and utilises rainwater for domestic, agricultural and industrial purposes. By capturing and filtering rainwater, this method reduces dependence on municipal water supplies and promotes eco-friendly water management.
Rainwater harvesting involves capturing runoff from rooftops, open surfaces, or catchment areas and channelling it through filtration systems into storage tanks or recharge pits. The collected water can be used for drinking, irrigation, flushing and industrial applications.
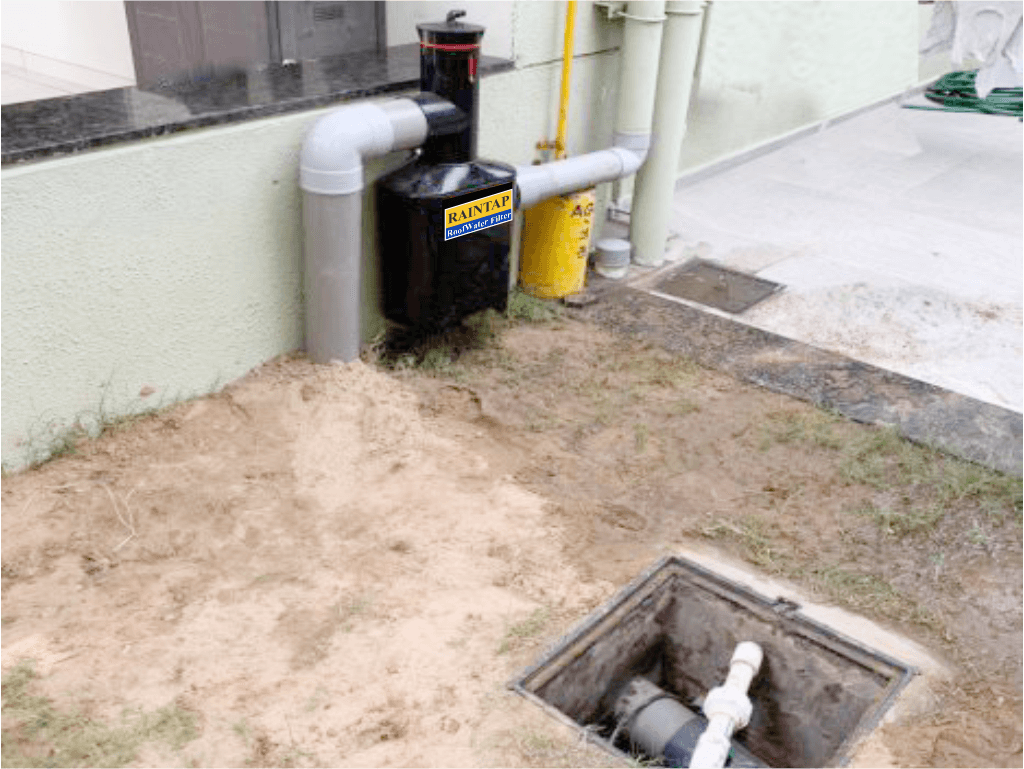

Advantages
The most important advantages of rainwater harvesting are:
- Reduces water bills: Minimises dependence on municipal water supplies.
- Prevents water runoff & erosion: Controls stormwater flow and reduces soil erosion.
- Eco-friendly & sustainable: Promotes responsible water conservation.
- Recharges groundwater: Helps maintain aquifers and underground water sources.
- Suitable for multiple uses: Provides clean water for irrigation, household use and industrial purposes.

Working Principle
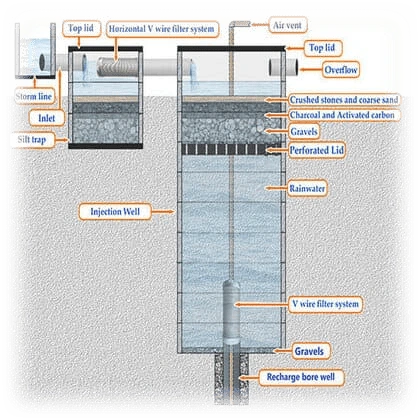
The components of a typical rainwater harvesting system include:
- Catchment area: The catchment area is where rainwater is collected. This can be a roof, parking lot or other impervious surface. The size and material of the catchment area affect the amount and quality of rainwater collected.
- Gutters and downspouts: Gutters collect rainwater from the catchment area and direct it to the downspouts. Downspouts carry rainwater from the gutters to the storage tank.
- Storage tank: Storage tanks can be above-ground or underground, and their size depends on the intended use and available space. Tanks can be made of various materials, such as plastic, metal or concrete.
- Treatment and filtration: Screens and filters remove debris, sediment, and contaminants from the rainwater. Additional treatment options may include sedimentation, filtration, disinfection or UV treatment.
- Distribution system: The distribution system delivers rainwater to the intended use, such as irrigation, toilet flushing or washing machines. Valves and controls regulate the flow of rainwater and prevent backflow into the potable water supply.
- Overflow and drainage: An overflow device allows excess rainwater to flow out of the storage tank during heavy rainfall events. A drainage system directs overflow water away from the building or surrounding areas.
- Monitoring system: Monitoring systems track water levels, flow rates and water quality.
The Sevarth USP
- No water loss
- Two stage filtration
- Non clogging filter
- Maintenance free
- Cost effective
- SS 304 filter element
- HDPE filter element
- User friendly
- No consumables
- Compact in size
- Fine filter for micro filtration
- Higher surface area for seamless flow
- Wall mounted
- Consistent in high and low intensity of rain